Structural Fat Grafting
What is fat grafting?
Fat grafting, also known as lipofilling or fat injections, is a plastic surgery technique which involves transfer of fat cells from one area of the body to another, on the same patient. It is a safe and very efficient technique, which is widely used in both aesthetic and reconstructive surgery.
Fat cells can be considered as our body’s own filler and as such, it can serve as a method to improve (or restore) contour and shape in a number of body areas. The amount of fat grafting can vary from a few cc (for face) to large volumes (for buttock or breast augmentation).
Although fat grafting can be performed as a sole procedure, most of the time it is used as an adjunctive to other procedures such as; breast implants and revision surgery, facelift, blepharoplasty, scar revision and many more.
How is it performed?
The fat is taken (harvested) by performing liposuction to selected areas of the body (donor sites). Most commonly abdomen, thighs, or flanks are used as donor sites.
The fat collected is then processed in order to remove most of the unwanted fluid. Finally, the processed fat is transferred to the recipient area by the means of small syringes, via tiny puncture skin incisions.
How much fat survives, and is it permanent?
The survival rate of the transferred fat varies depending on the amount, technique, and the vascularity of the recipient area. As an average, only 50-60 % of the transferred fat survives by regaining blood supply in its new location, and the rest gets naturally absorbed by the body.
Survival rates are higher for small amounts of transfer. Those fat cells that survive this initial process will permanently remain in the recipient area. Of note, the transferred fat will behave as the other fat cells from their original location in the body, hence they are subject to changing their volume according to weight loss or gain.
The survival rate of fat can be decreased by smoking, anti-inflammatories and previous treatments and scarring in the recipient area.
What are the indications?
Mr Orfaniotis is commonly using fat grafting in a number of breast and facial procedures:
Breast augmentation, both on it’s own or in combination with implants.
Fat transfer can be combined with implants in a procedure known as composite, or hybrid breast augmentation. In a composite augmentation following implant insertion fat grafting can be added to key areas such as the upper pole and cleavage. This combination can give a superior and more natural result, especially for patients that have very little breast tissue.
In selected cases, fat grafting can also be used for a natural breast enhancement without an implant. This approach requires larger amounts of fat harvested and it is best suited for those patients seeking small enlargements - maximum 1 cup size. It has the advantage of virtually no scarring , however for enhanced results the fat grafting procedure may need to be repeated a number of times, with 4 month intervals. Thin patients with limited donor site reserve and patients with saggy breasts are not good candidates for a “fat only” breast augmentation.
Read here about breast augmentation with implants.
Breast implant revision surgery
Adding some fat (100 - 150cc per breast) works extremely well in revisional surgery. The advantages are:
1. Provides extra volume allowing to use a smaller implant. This is important as a big implant will increase the risk of complications.
2. The fat is placed selectively into critical areas such as the upper pole/ cleavage and improves the shape and aesthetics.
3. Fat is mixed with stem-cells, which have a rejuvenating effect on the skin, making the breasts look more youthful.
4. Adding some of your own tissue can be seen as an investment if you ever decide to remove the implants without replacing them in the future
Breast uplift (mastopexy)
For patients who will benefit from a mastopexy / augmentation, lipofilling could be a great alternative to implants. The main drawbacks are the limitation in terms of volume, as well as the lack of structure of the volume added, as opposed to an implant. For larger volumes and for cases where more structure is needed, then an implant may be indicated.
Removal of implants
For those patient who opt to remove their implants without replacing them, lipofilling can provide some additional volume and enhance the outcome. This is usually combined with an auto-augmentation mastopexy technique at the same setting.
Although a simple removal procedure can improve some physical symptoms caused by implants, it can leave patients with poor aesthetic outcome. The result after implant removal surgery can be far superior when is combined with an auto-augmentation uplift and fat grafting.
What are the possible complications?
Fat grafting is a minimally invasive procedure, and as such the risk of complications is very small.
The main issue can be poor graft “take”, which will limit the success of the operation. This can happen when excessively large volumes (more than 250cc per breast) are used.
Other complications include:
Infection (very low risk). To reduce this risk you may be prescribed some antibiotics, especially if implants are also used.
Fat necrosis and oil cysts (hard lumps of poorly vascularised fat). Also rare. If these lumps are persistent they can be treated by either “fat dissolving injections” or minor surgery.
Liposuction complications at the donor site; bruising, swelling, bleeding, numbness, contour irregularities, asymmetry, poor aesthetic outcome
Fat embolism. This is an extremely rare but potentially fatal complication, if not recognised early. Fat embolism is the result of injecting the fat into large blood vessels. This risk is more significant in buttock augmentations (BBL), due to the size of the arteries and veins in the gluteal area. In breasts however, fat grafting is very safe as the vessels are of very small size and the risk of fat embolism is virtually zero.
Procedure Details.
- First appointment: £200
- Procedure Price: From £6800 - Depending on the amount required and the number of liposuction areas.
- Follow-up: No charge, appointments up to 1 year.
- Duration: 90-120 mins - Depending on additional procedures
- Anaesthetic: GA (fully asleep). Local anaesthetic can also be an option for small amounts in small areas.
- Length of stay: Day case (Home the same day). Overnight stay option also available
- Drains: No drains
- Recovery(for fat grafting only): 1 weeks to return to office work, 4 weeks to return to full activity. Can drive after 1 week
CASE EXAMPLES
Implant Revision surgery
10 year-old implants with severe capsular contracture and “Snoopy” breasts. Surgery involved exchange with a smaller implant, capsulectomy, mastopexy and fat grafting. 120cc of fat were injected to each breast.
The added fat not only has contributed to a far superior result, but also allowed for a smaller implant to be used, reducing the risk of future complications.
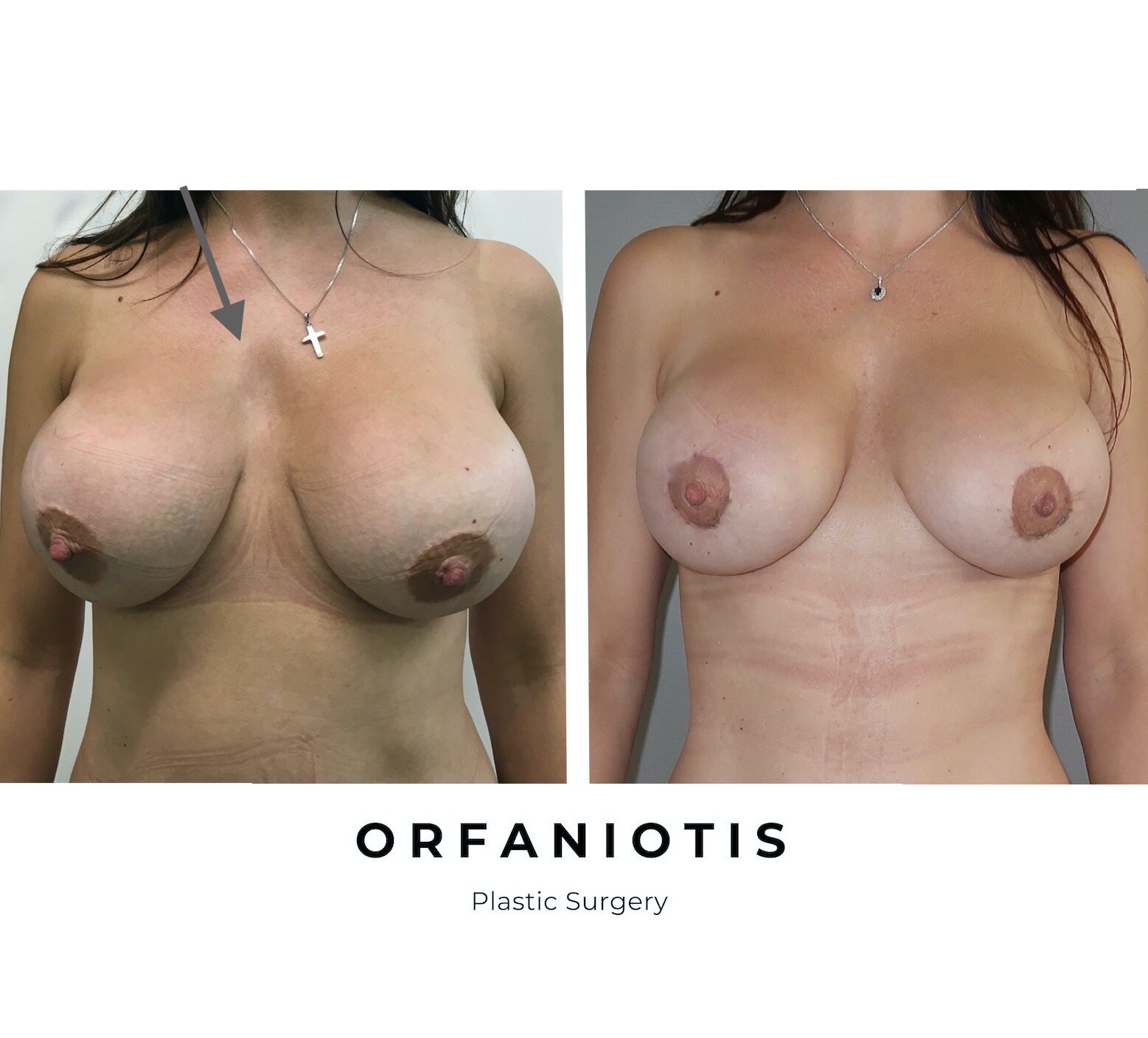
Revision surgery
This patient had implants placed 5 years ago by a different surgeon. She was not happy with the position of the nipple and most importantly the shape of her breasts on the upper pole and cleavage area (see grey arrow).
She was not keen at extensive surgery and scars. A peri-areolar (donut) nipple lift was carried out, along with a total of 240 cc fat grafting. The difference in both the shape and skin quality is noticeable in the after picture.